No matter which brand of truck you are loyal to, looking back at the company’s history, and more importantly the engine’s history, can be a deciding factor in future purchases. Knowing where your favorite brand’s engines came from can help give you a sense of where they might be going, and if purchasing an older engine, what you can expect to experience. Take for instance the Cummins diesel.
It has been around for several generations, and we thought it would be cool to give a history lesson about where the Cummins diesel engine originated and where it is today.
The Cummins Diesel: 1989 – 1998
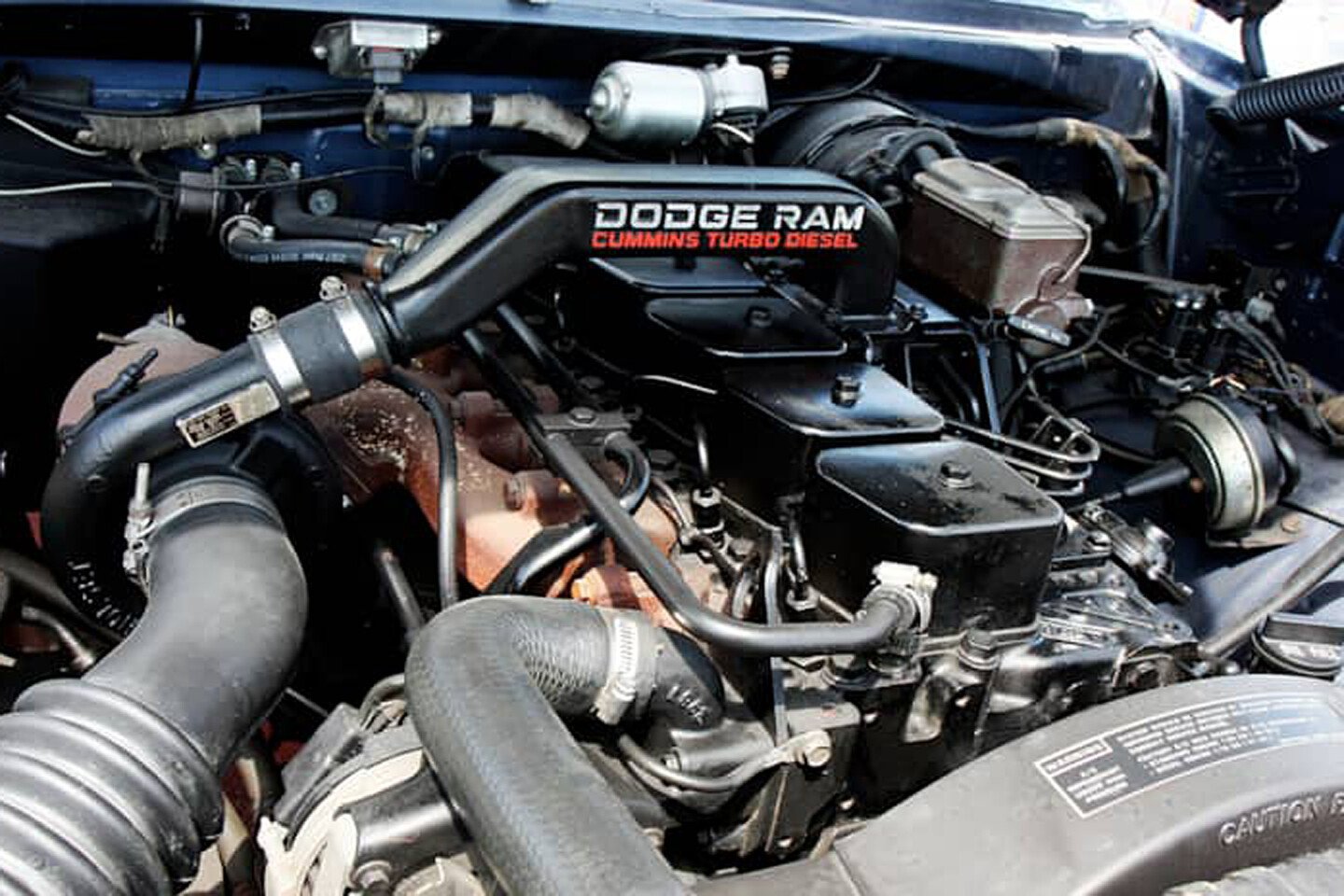
Ah, the beloved 12 valve. The first year Dodge offered a 5.9-liter Cummins diesel engine was 1989. These inline six-cylinder engines were direct-injected and turbocharged. Everything about this engine was drastically different than the competition. The Cummins was the only inline six-cylinder offered (still is), and the only direct-injected and turbocharged engine of “the big three.” The 5.9-liter featured two valves per cylinder (i.e. 12 valve) and utilized solid lifters. Between 1989 and 1993, the engine had a Bosch VE44 rotary injection pump. In 1994, the rotary pump was ditched for the infamous inline injection pump, the P7100 P-Pump.
12-Valve Engine Specs
- Bore: 4.02 inches
- Stroke: 4.72 inches
- Displacement: 359 cubic inches (5.9-liter)
- Injector: Direct Injection
- Pump: VE Rotary Pump (1989-1993); inline injection pump (P-Pump) (1994-1998)
- Turbo: Single Holset
- Base Horsepower and Torque
- 1989-1993:
- 160 hp at 2,500 rpm
- 400 lb-ft at 1,600 rpm
- 1994-1995:
- 160 hp at 2,500 rpm (auto)
- 400 lb-ft at 1,600 rpm (auto)
- 175 hp at 2,500 rpm (manual)
- 420 lb-ft at 1,600 rpm (manual)
- 1996-1998:
- 180 hp at 2,500 rpm auto/CARB
- 420 lb-ft at 1,600 rpm auto/CARB
- 215 hp at 2,600 rpm (manual)
- 440 lb-ft at 1,600 rpm (manual)
- Emissions: Catalytic Converter, CARB trucks EGR
The turbocharger used in this engine was the Holset H1C, which had a fixed geometry and a journal bearing. Although there were some variations throughout the production run, the most significant being the turbine housing and compressor wheel differences. Initially, an 18 cm2 turbine housing was used, but from ‘91.5 onwards, a 21 cm2 housing was introduced. However, due to complaints about low power and increased lag, the tighter 18 cm2 turbine housing was reintroduced from ‘92.5-’93. The factory setup provided a boost pressure of 18 psi.
Even with the addition of an intercooler, no horsepower and torque increase was made until 1994 when the P7100 P-Pump was added. Also, 1994 marked the addition of a catalytic converter, and in 1996, the California Air Research Board (CARB) emissions-certified trucks received an Exhaust Gas Recirculation (EGR) valve.
The presence of the P7100 injection pump marks the split horsepower ratings between manual and automatic transmissions.
The 12-valve Cummins diesel is a highly sought-after engine for enthusiasts looking to do a diesel swap. Whether it be into a truck or a car, the ease at which a 12-valve can be connected to nearly any car or truck makes it a great engine for a diesel swap.
One notable drawback of this engine, shared with all ’89-’02 engines, is the issue of the “Killer” Dowel Pin (KDP). During assembly, a small dowel pin was pressed into the block to locate the timing gear housing. Over time, due to vibrations and heat cycling, this dowel pin could work its way out of the block. Once free, it had the potential to come into contact with the cam gear, injection pump, and crank gears, leading to severe engine damage. While it might be challenging to access the dowel pin, securing it permanently in place inside the timing gear housing is highly recommended to prevent any potential issues.
Cummins Diesel: 1998 – 2002
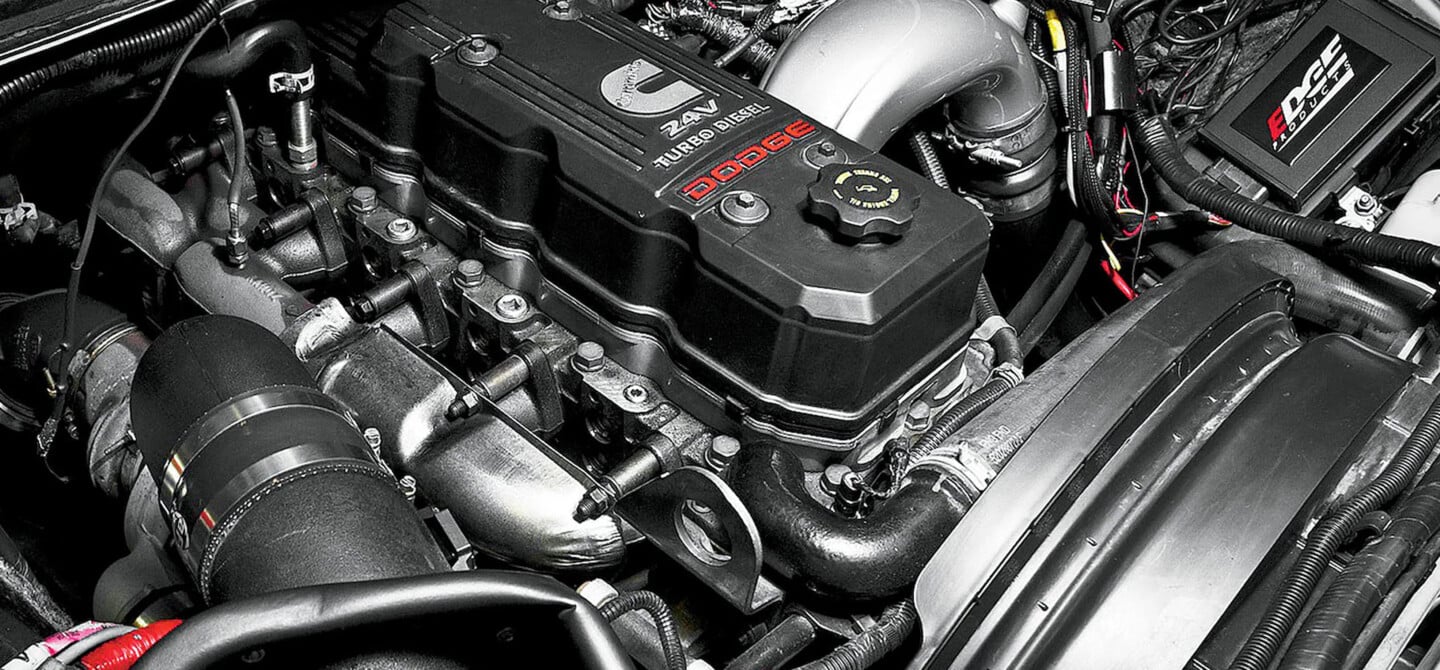
The Cummins diesel entered the computer age (well kind of) with the 24 valve. This next generation of Cummins to hit the market in 1998 brought quite a few changes with it. The two biggest changes were the addition of the VP44 electronically controlled rotary injection pump and the four-valve-per-cylinder head. While the injection pump was still primarily mechanical, the regulation of the pump was done electronically. Cummins referred to this new engine as an ISB (Interact System B-series), but enthusiasts have always called it the 24 valve.
24 Valve Engine Specs
- Bore: 4.02 inches
- Stroke: 4.72 inches
- Displacement: 359 cubic inches (5.9-liter)
- Injector: Direct Injection
- Pump: VP44 Rotary Pump
- Turbo: Single Holset
- Base Horsepower and Torque
- 1998-2000:
- 215 hp at 2,700 rpm (auto)
- 420 lb-ft at 1,600 rpm (auto)
- 235 hp at 2,700 rpm (manual)
- 460 lb-ft at 1,600 rpm (manual)
- 2001-2002:
- 235 hp at 2,700 rpm (auto/manual)
- 460 lb-ft at 1,600 rpm (auto/manual)
- 245 hp at 2,700 rpm (High Output)
- 505 lb-ft at 1,600 rpm (High Output)
- Emissions: Catalytic Converter, CARB trucks EGR
While most of the engine was actually redesigned, its basic configuration remained the same. There are some issues with this generation of engines. As with Ford and its head gasket problem in the 6.0’s, the 1998 to 2001 24 valves have block-cracking problems. This has been traced to faulty castings at one of the plants. All of the affected blocks have the number 53 embossed on them.
Common Rail Engine Specs
- Bore: 4.02 inches
- Stroke: 4.72 inches
- Displacement: 359 cubic inches (5.9-liter)
- Injector: Direct Injection
- Pump: Bosch CP3
- Turbo: Single Holset
- Base Horsepower and Torque
- 2003-2004:
- 235 hp at 2,700 rpm (CARB)
- 460 lb-ft at 1,400 rpm (Except H.O.)
- 250 hp at 2,900 rpm (Non-CARB)
- 460 lb-ft at 1,400 rpm (Except H.O)
- 305 hp at 2,900 rpm (High Output)
- 555 lb-ft at 1,400 rpm (High Output)
- 2004.5:
- 325 hp at 2,900 rpm (all)
- 600 lb-ft at 1,600 rpm (all)
- 2005-2007:
- 325 hp at 2,900 rpm (all)
- 610 lb-ft at 1,600 rpm (all)
- Emissions: Catalytic Converter and EGR vary by year.
2003-2007
The third revision of the 5.9-liter Cummins brought about a whole new standard in idle sound quality. The 24-valve engines are arguably the noisiest, and the new common rail engines were arguably the quietest (when they entered the market in 2003). The most notable improvement came from a new fuel system. The VP44 rotary injection pump was replaced with a Bosch CP3 high-pressure fuel pump feeding a single common high-pressure fuel rail. All of the injectors were connected to this fuel rail and saw the same high pressure. The injectors were now electronically controlled, allowing for multiple injection events during each combustion cycle. By using multiple injection events, the noise could be better controlled and regulated (it also helped with emissions).
From a structural standpoint, the engine block was strengthened and a bed plate was added. Most of the rotating assembly remained unchanged. The front timing cover and gear drives were changed to fit the CP3 fuel pump.
2007-2018
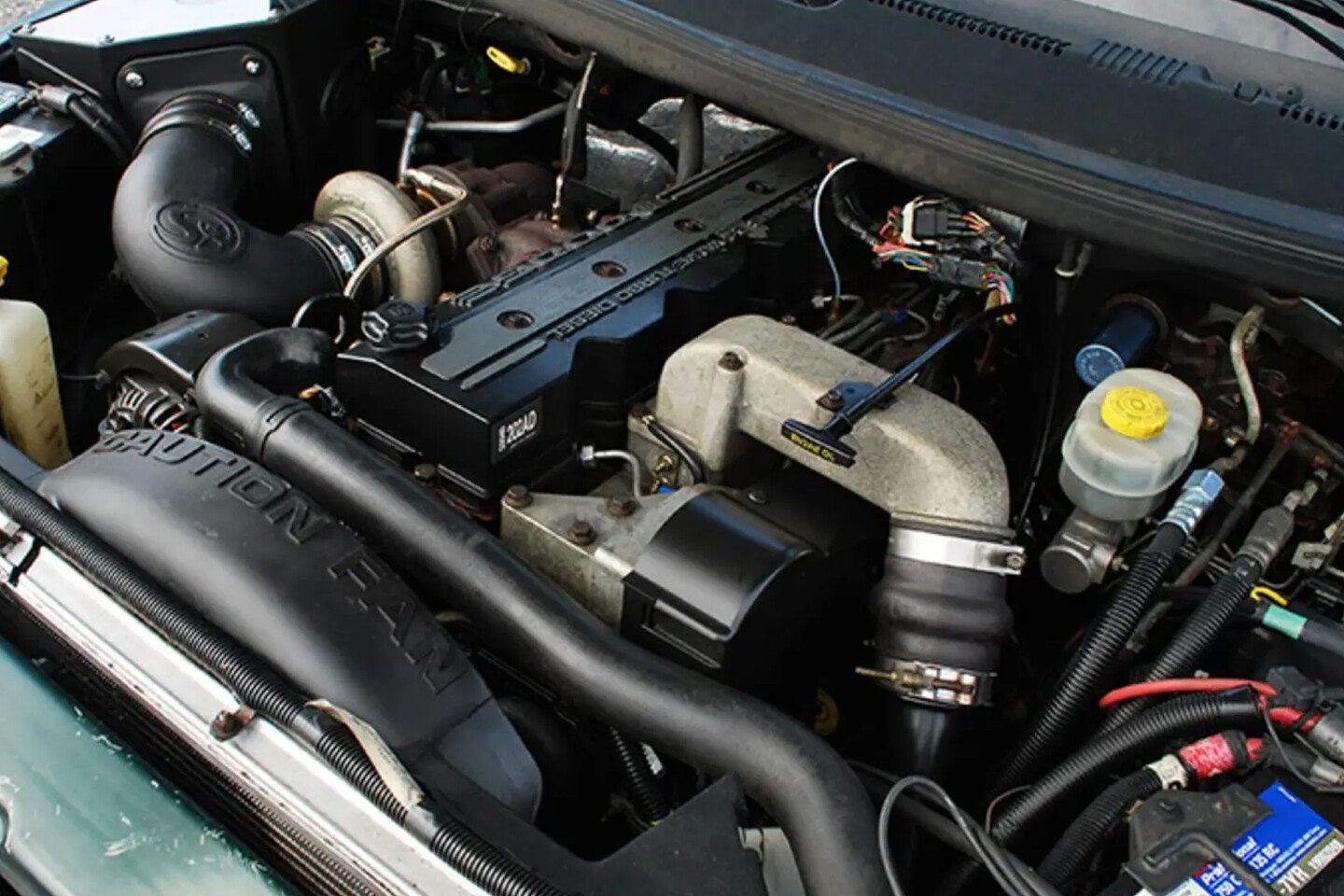
This marks the first major redesign of the 5.9-liter Cummins diesel since its introduction in 1989 in the Dodge Ram. The new 6.7-liter engine remained an inline six-cylinder with a bore of 4.21 (up from 4.02) inches and a new, longer stroke of 4.88 inches (up from 4.72). Feeding all of that additional displacement is a Variable Geometry Turbocharger (VGT) which helps create boost down low by changing the internal vanes to increase the pressure of the exhaust gasses contacting the turbine blade. On the big end, the vanes open up, helping to reduce back pressure to support top-end horsepower. The engine meets 2010 emissions, which means that the engine features an Exhaust Gas Recirculation (EGR) cooler, Diesel Particulate Filter (DPF), and catalytic converter.
A huge effort was spent quieting the engine, and the 6.7-liter Cummins diesel is actually 50-percent quieter than the previous generation’s 5.9-liter. In addition, for the first time, a factory exhaust brake is optional.
- What was the historical significance of the first-generation Cummins engine?
The first-generation Cummins engine, despite being introduced on an older AD Dodge chassis, was considered revolutionary at the time. It was light-years ahead of the competition, introducing features like a turbocharger, direct injection, and high torque output, setting new standards in the industry. - What were the durability characteristics of the first-generation Cummins engine?
The first-generation Cummins engine had a reputation for durability, thanks to its cast-iron block and forged steel rods, which were known for their strength and reliability. - What specific features did the first-generation Cummins engine have that Ford and GM did not offer on their V8 diesels?
The first-generation Cummins engine packed a turbocharger, direct injection, and 400 lb-ft of torque, which were not offered by Ford or GM on their V8 diesel engines. - What were the power output and torque figures of the first-generation 5.9L inline-six Cummins engine?
The first-generation 5.9L Cummins engine came stock with 160 horsepower and 400 lb-ft of torque.
Cummins Diesel: Then And Now
The history of the Cummins and Chrysler business venture spans over 30 years, making it one of the most successful collaborations in the automotive industry. Beginning sometime in the late 1980s, Cummins and Chrysler joined forces to forge a strong partnership that would have a profound impact on the automotive landscape. During this time, Cummins became the trusted supplier of its renowned diesel engines to Chrysler, specifically for use in trucks weighing over half a ton.
6.7 Engine Specs
- Bore: 4.21 inches
- Stroke: 4.88 inches
- Displacement: 408 cubic inches (6.7-liter)
- Injector: Direct Injection
- Pump: CP3 Bosch high-pressure fuel pump
- Turbo: VGT turbo
- Base Horsepower and Torque
- 2007-2010:
- 350 hp at 3,000 rpm (all)
- 650 lb-ft at 1,500 rpm (auto)
- 610 lb-ft at 1,500 rpm (manual)
- 2011-2012:
- 350 hp at 3,000 rpm (all)
- 800 lb-ft at 1,600 rpm (auto)
- 610 lb-ft at 1,500 rpm (manual)
- 2013- present:
- 350 hp at 2,800 rpm (manual)
- 660 lb-ft at 1,500 rpm (manual)
- 370 hp and 2,800 rpm (68RFE auto)
- 800 lb-ft at 1,700 rpm (68RFE auto)
- 385 hp at 2,800 rpm (Aisin AS69RC auto)
- 850 lb-ft at 1,700 rpm (Aisin AS69RC auto)
- Emissions: Catalytic Converter, EGR, and DPF.
These trucks boast an exceptional 80-percent take rate, further emphasizing the enduring popularity and quality of the vehicles produced through this enduring partnership. The journey of the Cummins and Chrysler business venture is a testament to the mutual trust, innovation, and success that can be achieved by combining industry-leading expertise. Together, they have left an indelible mark on the automotive industry and have solidified their reputation as pioneers in their respective fields.